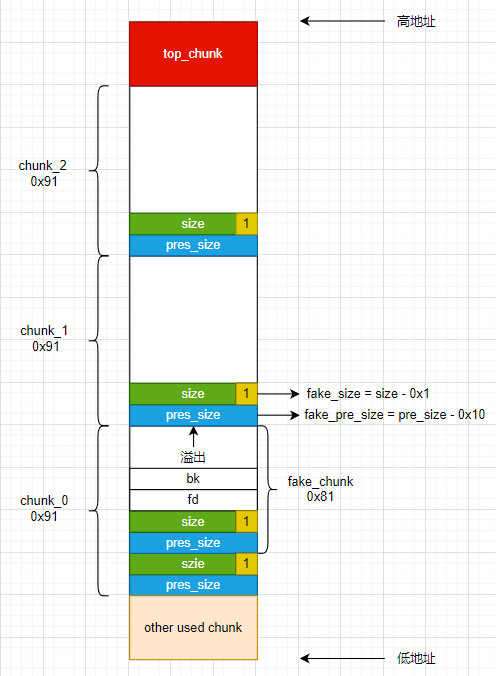
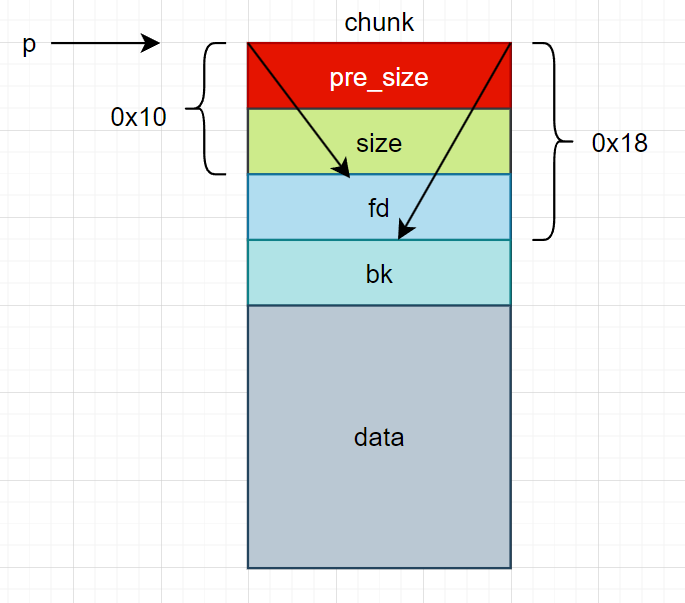
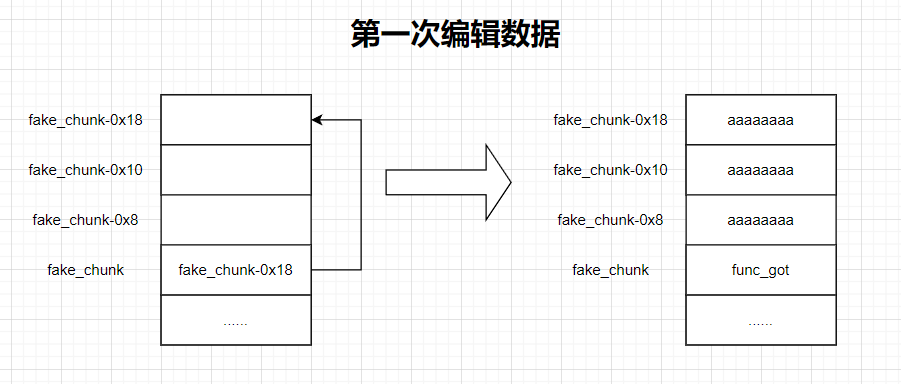
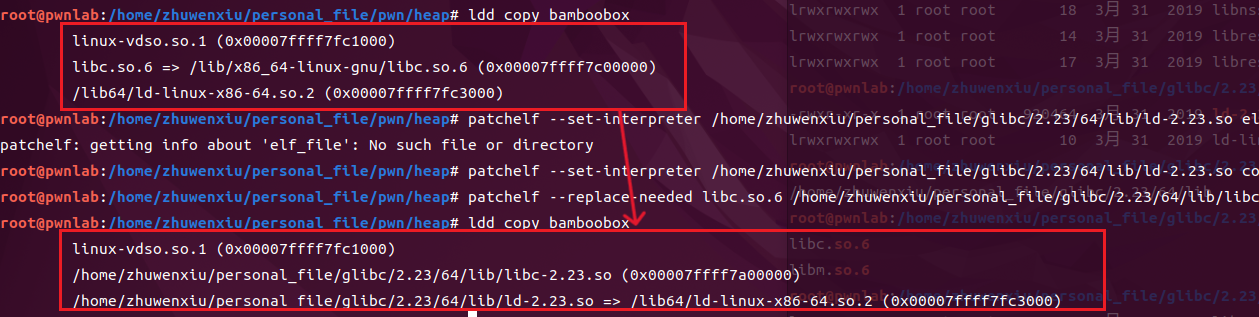
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
|
// free from /malloc/malloc.c
static void
_int_free (mstate av, mchunkptr p, int have_lock)
// av为内存状态分配器的状态 p为chunk指针 have_lock指示当前线程是否有arena的锁,多线程下依据此参数避免竞争条件
{
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* its size */
mfastbinptr *fb; /* associated fastbin */
mchunkptr nextchunk; /* next contiguous chunk */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize; /* its size */
int nextinuse; /* true if nextchunk is used */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsize; /* size of previous contiguous chunk */
mchunkptr bck; /* misc temp for linking */
mchunkptr fwd; /* misc temp for linking */
size = chunksize (p);
/* Little security check which won't hurt performance: the
allocator never wraps around at the end of the address space.
Therefore we can exclude some size values which might appear
here by accident or by "design" from some intruder. */
// 安全性检查:确保指针p不越界,也不处于无效的地址空间
if (__builtin_expect ((uintptr_t) p > (uintptr_t) -size, 0)
|| __builtin_expect (misaligned_chunk (p), 0))
malloc_printerr ("free(): invalid pointer");
/* We know that each chunk is at least MINSIZE bytes in size or a
multiple of MALLOC_ALIGNMENT. */
// 检查chunk的大小是否符合最小分配单位以及内存对齐的要求
if (__glibc_unlikely (size < MINSIZE || !aligned_OK (size)))
malloc_printerr ("free(): invalid size");
check_inuse_chunk(av, p); // 检查in_use标志位
#if USE_TCACHE // 如果启用了tcache机制,则优先使用tcache处理
{
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (size);
if (tcache != NULL && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
/* Check to see if it's already in the tcache. */
// 检查tcache中是否已经包含此chunk,避免双重释放
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (p);
/* This test succeeds on double free. However, we don't 100%
trust it (it also matches random payload data at a 1 in
2^<size_t> chance), so verify it's not an unlikely
coincidence before aborting. */
if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache_key)) // 检查key
{
tcache_entry *tmp;
size_t cnt = 0;
LIBC_PROBE (memory_tcache_double_free, 2, e, tc_idx);
for (tmp = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tmp;
tmp = REVEAL_PTR (tmp->next), ++cnt)
{
if (cnt >= mp_.tcache_count)
malloc_printerr ("free(): too many chunks detected in tcache");
if (__glibc_unlikely (!aligned_OK (tmp)))
malloc_printerr ("free(): unaligned chunk detected in tcache 2");
if (tmp == e)
malloc_printerr ("free(): double free detected in tcache 2");
/* If we get here, it was a coincidence. We've wasted a
few cycles, but don't abort. */
}
}
if (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
{
tcache_put (p, tc_idx); // 放入tcachebin
return;
}
}
}
#endif
/*
If eligible, place chunk on a fastbin so it can be found
and used quickly in malloc.
*/
// 检查chunk是否可以放入fastbin
if ((unsigned long)(size) <= (unsigned long)(get_max_fast ())
#if TRIM_FASTBINS
/*
If TRIM_FASTBINS set, don't place chunks
bordering top into fastbins
*/
&& (chunk_at_offset(p, size) != av->top)
#endif
) {
if (__builtin_expect (chunksize_nomask (chunk_at_offset (p, size))
<= CHUNK_HDR_SZ, 0)
|| __builtin_expect (chunksize (chunk_at_offset (p, size))
>= av->system_mem, 0))
{
bool fail = true;
/* We might not have a lock at this point and concurrent modifications
of system_mem might result in a false positive. Redo the test after
getting the lock. */
if (!have_lock)
{
__libc_lock_lock (av->mutex);
fail = (chunksize_nomask (chunk_at_offset (p, size)) <= CHUNK_HDR_SZ
|| chunksize (chunk_at_offset (p, size)) >= av->system_mem);
__libc_lock_unlock (av->mutex);
}
if (fail)
malloc_printerr ("free(): invalid next size (fast)");
}
free_perturb (chunk2mem(p), size - CHUNK_HDR_SZ);
atomic_store_relaxed (&av->have_fastchunks, true);
unsigned int idx = fastbin_index(size);
fb = &fastbin (av, idx);
/* Atomically link P to its fastbin: P->FD = *FB; *FB = P; */
mchunkptr old = *fb, old2;
if (SINGLE_THREAD_P)
{
/* Check that the top of the bin is not the record we are going to
add (i.e., double free). */
if (__builtin_expect (old == p, 0))
malloc_printerr ("double free or corruption (fasttop)");
p->fd = PROTECT_PTR (&p->fd, old);
*fb = p;
}
else
do
{
/* Check that the top of the bin is not the record we are going to
add (i.e., double free). */
if (__builtin_expect (old == p, 0))
malloc_printerr ("double free or corruption (fasttop)");
old2 = old;
p->fd = PROTECT_PTR (&p->fd, old);
}
while ((old = catomic_compare_and_exchange_val_rel (fb, p, old2))
!= old2);
/* Check that size of fastbin chunk at the top is the same as
size of the chunk that we are adding. We can dereference OLD
only if we have the lock, otherwise it might have already been
allocated again. */
if (have_lock && old != NULL
&& __builtin_expect (fastbin_index (chunksize (old)) != idx, 0))
malloc_printerr ("invalid fastbin entry (free)");
}
/*
Consolidate other non-mmapped chunks as they arrive.
*/
else if (!chunk_is_mmapped(p)) {
/* If we're single-threaded, don't lock the arena. */
if (SINGLE_THREAD_P)
have_lock = true;
if (!have_lock)
__libc_lock_lock (av->mutex);
nextchunk = chunk_at_offset(p, size);
/* Lightweight tests: check whether the block is already the
top block. */
if (__glibc_unlikely (p == av->top))
malloc_printerr ("double free or corruption (top)");
/* Or whether the next chunk is beyond the boundaries of the arena. */
if (__builtin_expect (contiguous (av)
&& (char *) nextchunk
>= ((char *) av->top + chunksize(av->top)), 0))
malloc_printerr ("double free or corruption (out)");
/* Or whether the block is actually not marked used. */
if (__glibc_unlikely (!prev_inuse(nextchunk)))
malloc_printerr ("double free or corruption (!prev)");
nextsize = chunksize(nextchunk);
if (__builtin_expect (chunksize_nomask (nextchunk) <= CHUNK_HDR_SZ, 0)
|| __builtin_expect (nextsize >= av->system_mem, 0))
malloc_printerr ("free(): invalid next size (normal)");
free_perturb (chunk2mem(p), size - CHUNK_HDR_SZ);
/* consolidate backward */ // 向前合并chunk即合并上一个chunk
if (!prev_inuse(p)) {
prevsize = prev_size (p);
size += prevsize;
p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize)); // p指针指向上一个chunk
if (__glibc_unlikely (chunksize(p) != prevsize))
malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size while consolidating");
unlink_chunk (av, p);
}
if (nextchunk != av->top) {
/* get and clear inuse bit */
nextinuse = inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, nextsize); // 检查下一个chunk是否被使用
/* consolidate forward */ // 向后合并chunk即合并下一个chunk,p指针不用移动
if (!nextinuse) {
unlink_chunk (av, nextchunk);
size += nextsize;
} else
clear_inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, 0);// 清除in_use标志位
/*
Place the chunk in unsorted chunk list. Chunks are
not placed into regular bins until after they have
been given one chance to be used in malloc.
*/
// 将chunk放入unsorted bin
bck = unsorted_chunks(av);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck))
malloc_printerr ("free(): corrupted unsorted chunks");
p->fd = fwd;
p->bk = bck;
if (!in_smallbin_range(size)) // 检查chunk大小是否属于small bins
{
p->fd_nextsize = NULL;
p->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
bck->fd = p;
fwd->bk = p;
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot(p, size);
check_free_chunk(av, p);
}
/*
If the chunk borders the current high end of memory,
consolidate into top
*/
// chunk如果和top_chunk相邻合并到top_chunk
else {
size += nextsize;
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
av->top = p;
check_chunk(av, p);
}
/*
If freeing a large space, consolidate possibly-surrounding
chunks. Then, if the total unused topmost memory exceeds trim
threshold, ask malloc_trim to reduce top.
Unless max_fast is 0, we don't know if there are fastbins
bordering top, so we cannot tell for sure whether threshold
has been reached unless fastbins are consolidated. But we
don't want to consolidate on each free. As a compromise,
consolidation is performed if FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD
is reached.
*/
// 超过合并阈值的chunk的合并
if ((unsigned long)(size) >= FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD) {
if (atomic_load_relaxed (&av->have_fastchunks))
malloc_consolidate(av);
if (av == &main_arena) {
#ifndef MORECORE_CANNOT_TRIM
if ((unsigned long)(chunksize(av->top)) >=
(unsigned long)(mp_.trim_threshold))
systrim(mp_.top_pad, av);
#endif
} else {
/* Always try heap_trim(), even if the top chunk is not
large, because the corresponding heap might go away. */
heap_info *heap = heap_for_ptr(top(av));
assert(heap->ar_ptr == av);
heap_trim(heap, mp_.top_pad);
}
}
if (!have_lock)
__libc_lock_unlock (av->mutex);
}
/*
If the chunk was allocated via mmap, release via munmap().
*/
else {
munmap_chunk (p); // 通过mmap分配的chunk用mumap释放
}
}
|